| |
| The
Mechanism Of Yogasana:
|
 |
|
|
|
Voluntary
efforts of the aasana.
|
|
|
|
Sensory
impulses to the medulla, mid-brain, cerebellum, basal
ganglion (centers for posture and equilibrium).
|
|
|
|
Sensory
impulses to the concerned muscles and joints.
|
|
|
|
Increase
in tension in the muscles and joints.
|
|
|
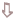
|
|
Duration of the final posture.
|
Duration of the final posture.
|
|
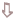
|
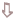
|
|
Gradually increased.
|
Increased suddenly.
|
|
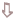
|
|
|
Effortlessness
and relaxation brought by yoga.
|
Fatigue, exhaustion.
|
|
|
|
|
Reduction
of muscular tension.
|
Increase in oxygen and energy.
Activity due
to increase in muscular tension.
|
|
|
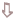
|